The Role of Traffic Signs in Modern Mobility
Traffic signs have been a fundamental part of transportation systems for more than a century, serving as the silent guides that help drivers, cyclists, and pedestrians move safely and efficiently. Traditionally, these signs were static objects made from simple reflective materials and mounted on poles. They conveyed instructions, warnings, or information with text and universally recognized symbols. While effective, conventional traffic signs face limitations in an era defined by rapid advances in materials science, smart technology, and connected vehicles. As we move into 2025 and beyond, traffic signs are entering a period of significant transformation, driven by innovations in sustainability, digital communication, and sensor integration. This evolution will redefine how roads communicate with both humans and machines.
Advanced Materials for Stronger and Greener Signs
The first major shift in traffic sign technology is the adoption of advanced materials. Historically, aluminum has been the standard substrate because it is lightweight, durable, and resistant to corrosion. Reflective sheeting enhanced nighttime visibility, but it required maintenance and eventually degraded under exposure to UV light, harsh weather, and pollution. In 2025, researchers and manufacturers are pushing toward composites and smart materials that can improve performance while reducing environmental impact. One promising development is the use of recycled polymers combined with graphene or carbon nanotubes, which provide exceptional strength and longevity while keeping production costs manageable. These composites can also reduce dependence on mined metals, aligning with broader sustainability goals. Additionally, photoluminescent coatings are being tested as an alternative to traditional retroreflective surfaces. These coatings absorb daylight and release it slowly after dark, maintaining visibility without relying entirely on headlights. This passive illumination not only saves energy but also improves visibility for autonomous vehicles equipped with light-sensitive sensors.
Sustainability and Lifecycle Innovation
Sustainability is not only about the materials themselves but also about the production and lifecycle of traffic signs. Cities around the world are aiming to lower carbon footprints, and road infrastructure is no exception. By 2025, more municipalities are incorporating recyclable substrates, eco-friendly inks, and modular designs that allow damaged portions of a sign to be replaced instead of discarding the entire unit. Some manufacturers are experimenting with biodegradable materials for temporary traffic signs used in construction zones or events. These innovations address the growing need to balance infrastructure demands with environmental stewardship.
Smart Sensors and Two-Way Communication
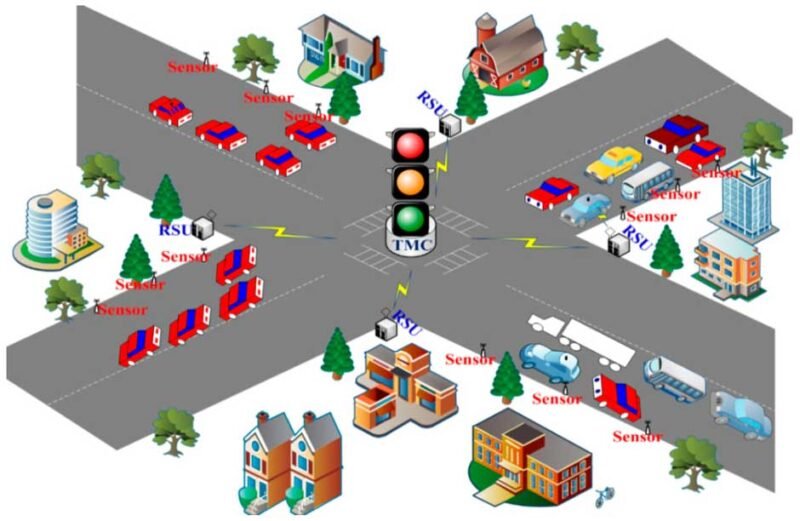
Alongside material advancements, traffic signs are becoming smarter thanks to embedded sensors and connectivity features. Traditional signs communicate only in one direction: from sign to human. In contrast, the next generation of traffic signs creates a two-way flow of information. Smart signs equipped with sensors can monitor environmental conditions, traffic density, and even structural integrity. For example, a smart stop sign could detect when visibility is poor due to fog or heavy rain and increase its brightness or trigger nearby streetlights to activate. Sensors embedded in speed limit signs can gather data on vehicle speed and automatically adjust limits based on congestion or road conditions.
IoT and Real-Time Traffic Management
Integration with the Internet of Things (IoT) is also transforming roadside communication. By 2025, many signs are expected to be linked to central traffic management systems, where data collected from roads can inform real-time decision-making. Variable message signs that once relied on manual input or preprogrammed schedules can now update instantly based on live data. If a lane closure occurs due to an accident, connected signs can display detour instructions within seconds, reducing delays and enhancing safety. For connected and autonomous vehicles, this shift is even more important. Vehicle-to-everything (V2X) communication relies on data exchanges between infrastructure and cars. Smart traffic signs can transmit their status and instructions directly to a vehicle’s onboard system, ensuring drivers and autonomous vehicles receive timely, accurate updates even if weather, distance, or obstructions reduce visibility.
Energy-Harvesting Traffic Signs
Another fascinating trend is the exploration of energy-harvesting traffic signs. Solar-powered signs are already common in certain regions, especially for pedestrian crossings and school zones. However, in 2025, energy harvesting is expanding beyond solar panels. Researchers are developing piezoelectric systems that capture vibrations from passing vehicles, converting kinetic energy into electricity to power embedded LEDs or sensors. Similarly, wind-harvesting microturbines can capture energy from vehicle slipstreams, providing renewable power to traffic signs in areas with high traffic flow. These self-sufficient systems reduce the need for external power sources and can be deployed in remote locations where electricity is expensive or inaccessible.
Artificial Intelligence in Roadside Communication
Artificial intelligence is also beginning to play a role in the traffic sign ecosystem. While AI is most often associated with vehicles themselves, it can be applied to infrastructure to make signs more adaptive. For instance, AI-powered systems can analyze traffic flow data and dynamically adjust digital speed limits to smooth congestion or prevent accidents. In cities experimenting with smart grids, AI can coordinate traffic sign illumination to reduce energy consumption while still maintaining safety standards. Over time, these systems will learn from historical data to anticipate conditions, making road networks more efficient.
Challenges Facing Smart Traffic Signs
The evolution of traffic signs is not without challenges. One of the main concerns is cost. Advanced materials, embedded sensors, and connectivity require significant investment compared to traditional signs. Municipalities with limited budgets may struggle to adopt these technologies widely, leading to disparities between regions. Another challenge is maintenance. While smart traffic signs can diagnose their own faults, they still require specialized technicians to repair or replace components, adding complexity to municipal operations. Cybersecurity is another critical issue. As signs become part of interconnected systems, they are vulnerable to hacking or malicious interference. A compromised sign could display false information or disrupt traffic flow, so strong encryption and robust cybersecurity measures are essential.
Global Adoption and Regional Differences
Despite these challenges, the future of traffic signs is promising. The potential benefits include improved safety, more efficient traffic management, reduced environmental impact, and enhanced compatibility with autonomous vehicles. Globally, different regions are moving at different speeds toward adopting these technologies. In Europe, strict environmental regulations are accelerating the shift to sustainable materials and energy-efficient designs. In Asia, where megacities face chronic congestion, smart sensors and AI-driven traffic management are becoming priorities. In North America, pilot programs in cities like Los Angeles, Toronto, and Austin are experimenting with connected traffic signs that integrate with autonomous vehicle testing zones. These regional variations reflect local priorities but collectively signal a worldwide shift toward the future of roadside communication.
Machine-Readable Signs for Autonomous Vehicles
Looking further ahead, traffic signs may become less visible to human drivers and more oriented toward machine-readable communication. With the rise of fully autonomous vehicles, traditional visual signs could be supplemented or even replaced by digital infrastructure that communicates directly with vehicle systems. Machine-readable QR-like codes, RFID tags, or digital broadcasting systems could provide data invisible to the human eye but instantly interpretable by autonomous driving systems. For now, hybrid systems will dominate, ensuring that both humans and machines receive the information they need.
A Smarter Future for Safer Roads
In conclusion, the traffic signs of 2025 represent much more than static roadside objects. They embody a fusion of advanced materials, smart sensors, renewable energy, artificial intelligence, and connectivity. These innovations are creating a new era of roadside communication where signs not only guide but also interact, adapt, and respond in real time. While challenges around cost, maintenance, and security remain, the benefits for safety, efficiency, and sustainability are undeniable. As cities modernize infrastructure and prepare for the integration of autonomous vehicles, traffic signs will play a central role in shaping safer and smarter roads. The transformation we see today marks just the beginning of a future where the road itself becomes an intelligent partner in mobility.